
Forschungsprojekte

ICEBIO
ICEBIO is a PhD network that will train the next generation of experts in glacier microbiology and biogeochemistry. ICEBIO will provide a database of the functional diversity and potential of the glacier biome, which will not only greatly improve our understanding of a threatened biome, but also demonstrate the potential for exploiting economic and ecological services. Dr. Brill + Partner GmbH will, among other things, provide a risk assessment regarding pathogenic organisms from the glacier biome, including the inclusion of bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Further Information: https://www.icebio.eu/pages/project/index.html The ICEBIO Doctoral Network is supported by a grant from the European Commission’s MSCA Doctoral Network program under project number 101072761

CRM-geothermal
Dr. Brill+Partner GmbH is overly excited to participate in the european funded project CRM-geothermal (Raw materials from geothermal fluids: occurrence, enrichment, extraction) and to contribute our expertise to secure the supply of rare raw materials for Europe in a medium to long term perspective.

Antifouling - Preventive and postal measures to reduce marine and limnic fouling.
Grant number: 16KN108701 - Duration: 01.04.2021 - 30.09.2022
The guiding principle is the development of effective and efficient materials, methods and systems for the preventive prevention and subsequent removal of submarine fouling under environmentally compatible aspects. In terms of applicability, a combination of both physical and chemical methods is conceivable, as a low-maintenance and durable solution is desired. Thus, the solution should also be practicable in everyday use and, at best, be accepted as a new product on the market. It should also undergo initial testing to verify its effectiveness under realistic conditions. Successful results in the development of new anti-fouling systems should at best be adaptable to non-ship industries. Thus, other facilities in the industry are also affected by types of fouling and can benefit from these developments. This offers companies the opportunity to expand their market segment and open up new sectors of the economy. The optimal solution prevents fouling in the long term, is environmentally friendly and profitable for the user. This is a research project of the ZIM innovation network, for which Dr. Brill + Partner will not initially receive any funding.

Development of a standardized test method to evaluate the anti-adhesion properties of surfaces against biofilms on ship hulls.
Akronym: HaptoCheck - ZIM-Förderkennzeichen KK5193801KS0
The present project addresses the development of a test method for the adhesive strength of microbial coatings (biofilms) on ship hulls. Biofilms form the first stage of colonization of surfaces and create the basis for macroscopic fouling, which has a negative impact on fuel consumption in shipping. The main focus of the research project is initially to establish series of measurements on the detachment of biofilms from test surfaces as a function of wall shear stress. For this purpose, a laboratory-scale test apparatus will be produced to simulate the sailing speed of ships in practice. On this basis, abiotic model substances are to be developed, with the aid of which the adhesion of microbial surface coatings to antifouling coatings can be simulated in the test apparatus and used to quantify such effects as part of a standardized test procedure. On the basis of the test results, a final evaluation of the effectiveness of such coating systems is to be which should enable developers to optimize the non-stick properties of their products more cost-effectively and effectively. The resulting new test method is a screening test for estimating the effectiveness of antifouling systems. It is a seasonally independent rapid test procedure that will provide paint companies with quick results for further development. The procedure will not be able to replace the later semi-annual open water tests with the promising variants, but it will accelerate the development work of the companies.

A standardized test for determining the development of resistance in microorganisms to biocides
The aim of this project is to develop a standardized microbiological test method to determine the potential for emergence of resistance and cross-resistance in the use of surface disinfectants and antimicrobial surfaces. The focus is on the emergence of resistance to disinfectants and material protection agents through de novo mutations. These resistances may pose a particular risk because they confer cross-resistance to antibiotics. Disinfectants and antimicrobial material coatings are approved under the EU Biocides Regulation. The regulation provides for assessment of the risk of emergence of resistance and cross-resistance, but currently lacks standardized test methods to provide a framework for assessment by industrial applicants and assessing authorities. The test method to be developed in the project, based on efficacy tests for surface disinfection (DIN EN 13697:2019 and the DIN EN 16615:2015), will allow biocide manufacturers to have their product tested for resistance development by independent testing institutes. The results will enable authorities to make a better assessment of resistance risk in the context of authorization under the EU Biocides Regulation. The work is being carried out in cooperation with the Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM).

Verbundprojekt ROBUST
Supported by the Federal Ministry of Economics and Energy
For the joint project "ROBUST - Integrated Coating and Cleaning Concept for the Control of Fouling on Offshore Structures" a grant from the federal budget was approved. The joint project is part of the "Maritime Research Program" and is administratively and technically supervised by Project Management Jülich.
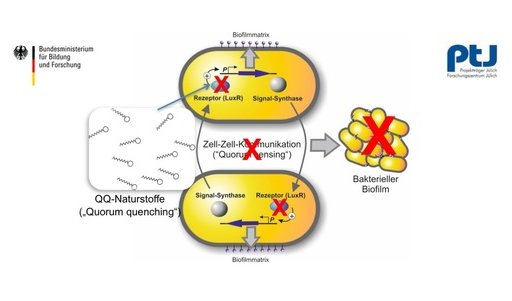
QQ - Naturstoffe
New antimicrobial agents against biofilms
We are pleased to be part of the joint project "QQ-Naturstoffe - New antimicrobial agents against biofilms". The project is part of the funding measure "National Research Strategy Bioeconomy 2030" of the Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Within this project, Dr. Brill + Partner GmbH deals with marine corrosion-inducing organisms that can cause long-term damage to technically relevant materials such as steel or concrete. In addition to the microbiological characterization of outsourced sample materials (in the laboratory or in the North Sea), fluorescence microscopic examinations (visualization of microbiological structures after doping with selective dyes) and atomic force microscopic measurements of the surfaces (topography, density and localization of the microbial fouling) are carried out in order to decide whether an anti-fouling effect is present or whether the integrity of the material can be maintained by the QQ-based anti-fouling measure used.

NLKWN
environmentally friendly design of washing areas in marinas near the coast
Using the Lower Saxony model harbours of Norderney and Oldenburg as examples, concepts were drawn up on how to deal with the washing water that is created in autumn when the pleasure boats are taken out of the water and washed. During this process, growth, but also residues of the antifouling coatings together with their biocides and microplastic components are detached and must be filtered and collected so that they cannot get into the marine environment or into the soil.
UBA-Forschungsprojekt
Certification of biocide-free antifouling systems for eco-labels
On behalf of the Federal Environment Agency (UBA), Dr. Brill + Partner GmbH Institute for Antifouling and Biocorrosion in cooperation with Hydrotox GmbH and LimnoMar will work on a research project until August 2021 in which award criteria for 1 to 2 environmental labels (Blue Angel) for biocide-free antifouling products will be developed.
See project details